End-User License Agreements (EULAs) form the foundation of the legal relationship between software providers and users. These critical documents establish the terms under which individuals or organizations access and use digital products. For corporate legal teams, understanding how to create, implement, and manage effective EULAs is essential for protecting intellectual property and limiting liability. This article explores the fundamentals of EULA agreements, their key components, and best practices for implementation.
What is an EULA agreement?
An End-User License Agreement (EULA) is a legal contract between a software developer or publisher and the end user. Unlike a purchase agreement for physical goods, an EULA does not transfer ownership of the software but instead grants a license to use it under specific conditions.
EULAs differ from other common legal documents such as Terms of Service and Privacy Policies in several important ways:
When a business distributes software, mobile apps, or SaaS solutions, implementing a comprehensive EULA becomes necessary to establish clear boundaries for product use and to protect the company’s assets.
Key components of an effective EULA
A well-crafted EULA includes several essential elements that protect both the business and its users. Understanding these components helps legal teams create agreements that are both protective and enforceable.
Usage rights and restrictions
This section defines what users are allowed to do with the software. It specifies whether the license is personal or commercial, if it applies to multiple devices, and any limitations on usage scope. Restrictions often address issues such as reverse engineering, code modification, and redistribution.
Intellectual property protection
Intellectual property clauses assert ownership of the software, content, and associated materials. These provisions clarify that users receive a license to use the product, not ownership of the underlying code or content. Additionally, they outline copyright protections and trademark usage guidelines.
Liability limitations and disclaimers
These clauses limit the company’s exposure to legal risks by defining the boundaries of responsibility. They typically include disclaimers of warranties, limitation of liability provisions, and indemnification requirements. Courts generally uphold these provisions when they are clearly presented and reasonable in scope.
Termination conditions
Termination clauses outline circumstances under which either party are allowed to end the license relationship. They specify the business’s right to terminate access if users violate the agreement terms and explain what happens to user data and content after termination.
Legal enforceability of EULAs
For an EULA to provide meaningful protection, it must be legally enforceable. Several factors influence enforceability across different jurisdictions.
Presentation methods and user consent
How users encounter and agree to an EULA significantly impacts its legal standing. The two primary presentation approaches are:
- Clickwrap agreements require users to actively indicate consent (usually by checking a box or clicking “I Agree”) before accessing the software. Courts consistently uphold properly implemented clickwrap agreements.
- Browsewrap agreements assume consent through continued use of the software without requiring explicit acknowledgment. These agreements face greater enforceability challenges, particularly when users have no reasonable opportunity to review the terms.
International considerations
For businesses operating across borders, EULA agreements must address international legal variations. Different countries maintain distinct requirements regarding consumer protection, intellectual property rights, and contract formation. Consequently, companies serving global markets often include choice of law provisions and jurisdiction clauses to control which legal standards apply.
Recent court cases demonstrate that EULAs with clear language, reasonable terms, and proper presentation methods generally withstand legal scrutiny. Conversely, agreements with hidden terms or excessively one-sided provisions face enforcement difficulties.
Common EULA mistakes to avoid
Legal teams frequently encounter several pitfalls when creating and implementing EULAs. Recognizing these common mistakes helps businesses develop more effective agreements.
Overly complex language
Many EULAs suffer from excessive legal jargon that confuses users and potentially undermines enforceability. Courts increasingly expect agreements to be reasonably understandable to average users. Therefore, balancing legal protection with readability becomes essential.
Inadequate coverage of critical issues
Some EULAs fail to address important aspects of the software relationship, such as data handling practices, third-party access, or user-generated content. These omissions create uncertainty and potential liability exposure.
Failure to update with changing laws
Privacy regulations, intellectual property statutes, and consumer protection laws evolve continuously. EULAs that remain static despite legal changes gradually lose effectiveness and compliance.
Best practices for creating and managing EULAs
Implementing these best practices helps legal teams develop and maintain effective EULA agreements.
Clear and accessible language
While legal precision remains important, successful EULAs use straightforward language wherever possible. Organizing content with headings, bullet points, and summaries improves user comprehension without sacrificing legal protection.
Comprehensive coverage of key issues
Effective EULAs address all relevant aspects of the software relationship, including:
Regular review and updates
Establishing a systematic review process ensures EULAs remain current with changing laws, business practices, and product features. Documentation of review dates and changes supports version control and demonstrates diligence if legal challenges arise.
Strengthening legal foundations through well-crafted EULAs
EULA agreements serve as the foundation for the legal relationship between software providers and users. When properly created and implemented, they protect intellectual property rights, limit liability exposure, and establish clear expectations for all parties.
For corporate legal teams, developing effective EULAs requires attention to content, presentation, and ongoing management. By following best practices and leveraging appropriate legal technology solutions, businesses strengthen their legal position while building trust with users.
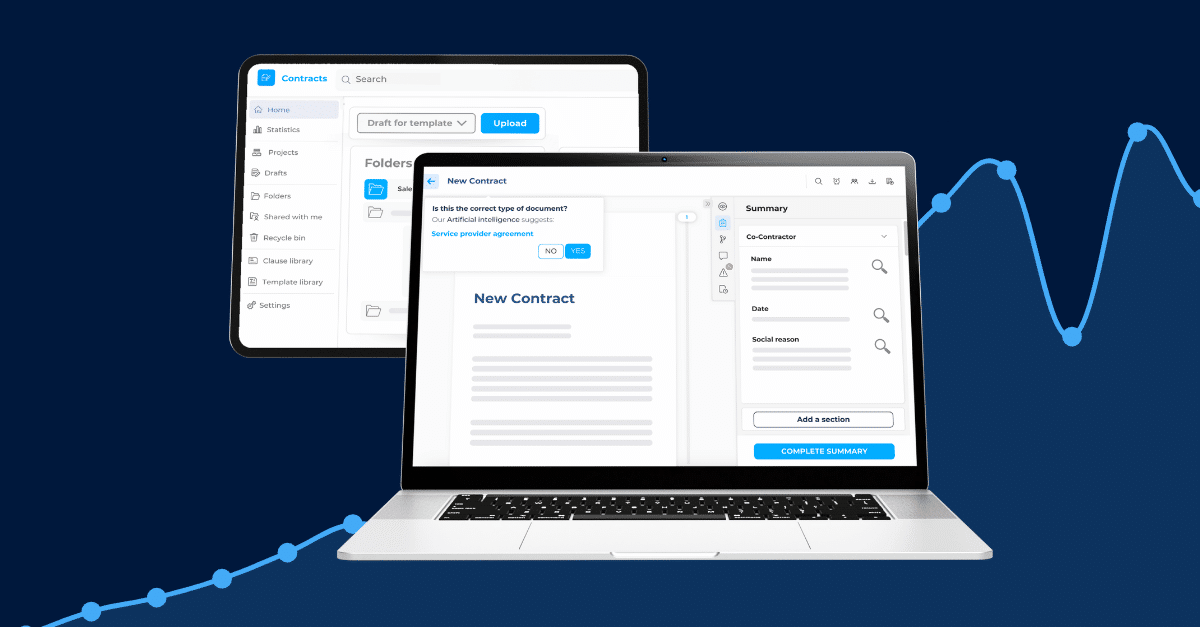
The DiliTrust Suite provides the tools legal departments need to create, manage, and update EULAs efficiently. The Contract Management module provides centralized storage and management of all legal agreements, including EULAs. With version control and collaboration features, legal teams maintain control over these critical agreements throughout their lifecycle.
Would you like to learn more about how DiliTrust can help your legal team streamline EULA and other legal agreement management? Discover how our secure solutions support effective legal operations.